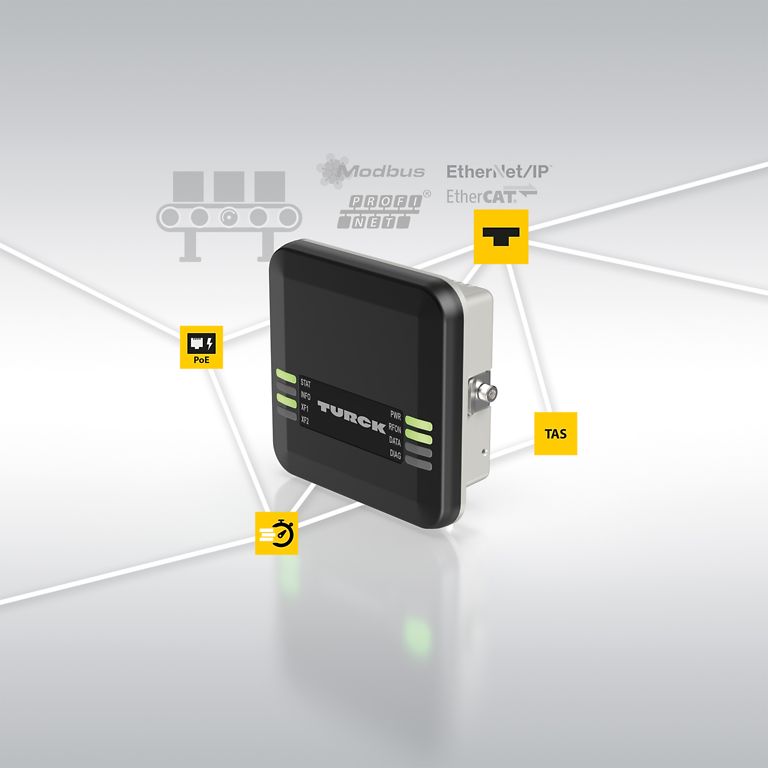
HF bus mode reduces costs for RFID applications
Whether a hose coupling station, ink cartridges, format or tool changes: RFID applications with many read/write heads can now be implemented in a particularly cost-effective and time-saving manner thanks to TURCK's HF bus mode — with just one cable up to ATEX zone 1/21
Quick read
RFID applications with a large number of read/write heads, such as female connector or hose coupling stations, are often expensive and time-consuming to install and maintain due to the required hardware. With the HF bus mode for its IP67 RFID interfaces, TURCK has created an efficient solution to this challenge. This function allows up to 32 HF read/write heads to be connected to each RFID input of an interface module. With four RFID channels per module, up to 128 read points can be detected and parameterized centrally. Together with TURCK's encapsulated TNR42/TC-EX HF RFID reader, the line topology can even be used in hazardous areas (zone 1/21).
Highly automated, flexible and networked industrial production requires efficient technologies for identifying systems, tools, workpieces and products – and smart data that will enable the digital transformation of production plants. In addition to sensors, preferably with IO-Link, and optical identification systems, the radio-based RFID identification technology plays a major role. RFID is regarded as a key technology for the smart factory and the Industrial Internet of Things IIoT, because it enables products, workpiece carriers or tools to be identified and localized clearly and without contact.
Robust Ethernet multi-protocol block I/O modules as RFID interface
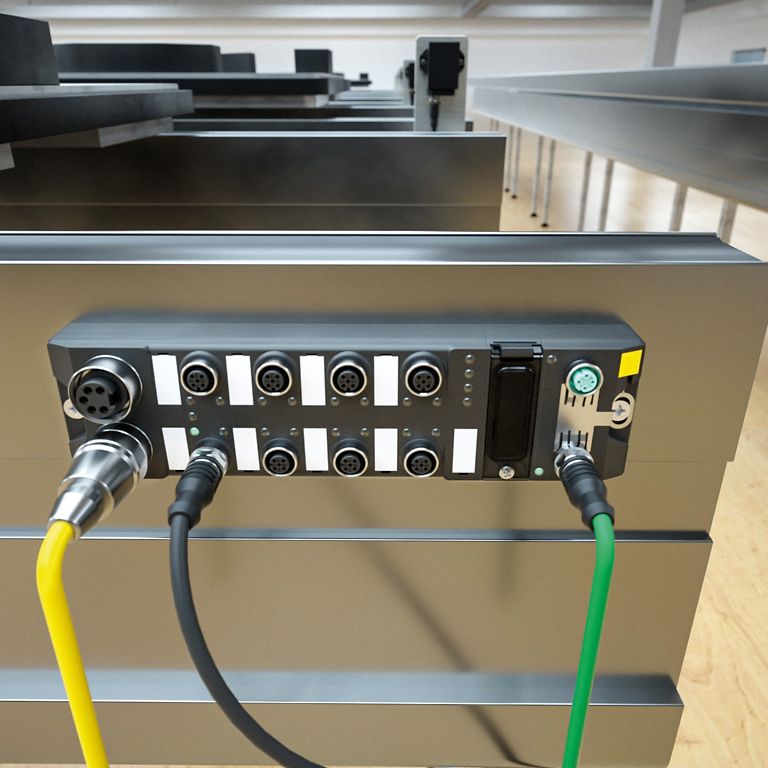
The implementation of RFID in production processes is often complicated and time-consuming. With its Ethernet RFID interfaces based on the block I/O families TBEN-L, TBEN-LL, TBEN-S and TBEC-LL, TURCK supports its customers in this area too. The multi-protocol devices allow the parallel operation of HF and UHF read/write heads and transfer the data to the control unit via PROFINET, EtherNet/IP or Modbus TCP. In this way, the modules facilitate applications with different requirements and reduce the required storage variety. A further RFID interface
for EtherCAT (TBEC) has recently been added to the portfolio. All RFID I/O modules are designed in a fully encapsulated plastic housing with IP67/IP69K protection and operate in an extended temperature range of -40 to +70 °C. This makes the robust modules suitable for direct installation on the machine, without the need for a control cabinet or switchgear.
Like the standard version of the TBEN-L modules, the particularly compact TBEN-S-RFID module can be easily implemented without special programming effort or function modules. Even without sending a command to the controller, for example, the UID or memory areas of the tags can be read and transmitted, triggered by the read-write device. The integrated web server allows a function test or commissioning without a control system. The CODESYS-programmable TBEN-L variant offers control functions and can thus filter RFID data directly on site, pre-process it and, if desired, also link it directly to control actions. TURCK also offers the TBEN-L-RFID interface with Linux in a version for system integrators. The TBEN-L-RFID interface is also available with an integrated OPC UA server that follows the Auto-ID Companion Specification.
In addition to four RFID ports, the TBEN-L modules also provide eight universal DXP I/O channels to which sensors, signal lights or other actuators can be connected. All connections are designed as M12 connectors; the power supply is provided via 7/8-inch connectors in the L versions, and for the LL versions for L-coded M12 connectors for future-proof M12 power technology.
HF bus mode allows 128 read/write heads per interface
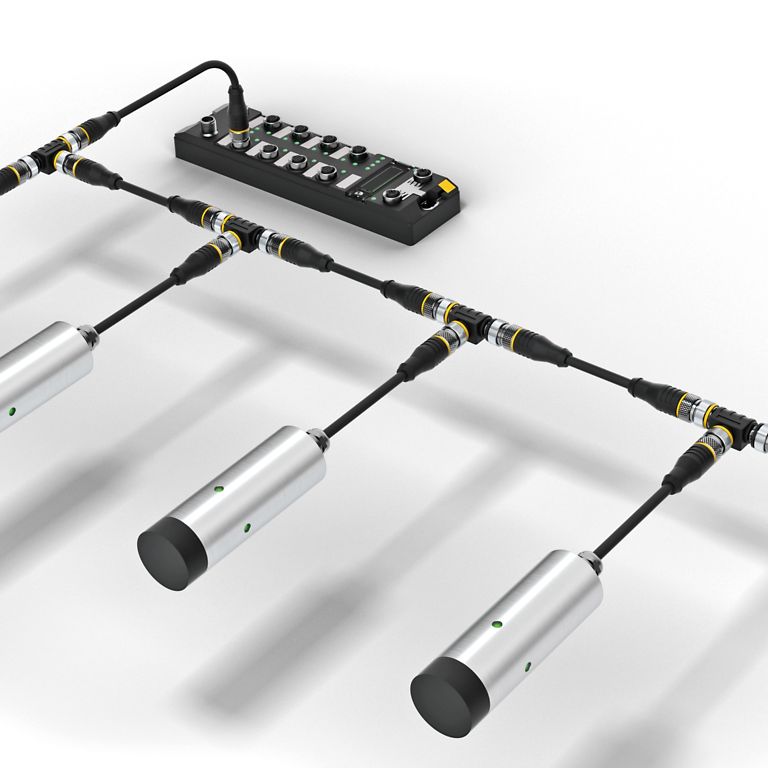
TURCK's TBEN interfaces, as well as the EtherCAT TBEC interface, impress with a very special feature: the HF bus mode, particularly in applications where numerous HF read/write heads are used in a small space. Since this function does not require a point-to-point connection in comparison to IO-Link, it enables the user to connect up to 32 suitable HF read/write heads in series on each of the four RFID ports. This significantly reduces wiring and costs in applications with many read/write positions.
The wiring is very simple using a line topology. A total cable length of up to 50 meters can be connected per RFID port. The read/write heads can branch off the main line via 2-meter-long spur lines. This makes the system easy to install and expand. Each of the 32 read/write heads can be addressed individually in HF bus mode to execute a wide range of commands such as read, write or inventory. The read/write heads can be addressed both manually and automatically. When individual read/write heads are replaced, automatic addressing takes place in ascending order according to the connection sequence. Thanks to the lower use of modules and cables, the user benefits not only from cost savings, but also from shorter assembly and commissioning times.
High performance in Continuous mode with Track & Trace
Continuous HF bus mode is similar to HF bus mode in terms of design and cost advantage, but all read/write heads are activated at the same time. Therefore, the Continuous mode is suitable for both static and slow dynamic applications, such as reading or writing tags in parallel, due to its higher performance. The individual read/write heads store the read data in a buffer until the RFID interface queries it cyclically one after the other. The data is stored in the FIFO memory of the interface and can be retrieved by the control system using the "Read data from buffer" command.
With the "Track & Trace" function, Continuous HF bus mode opens up new fields of application – for example in logistics or conveyor technology. This includes parallel detection in multi-track transfer/conveyor systems, for products with different position heights of the tag in a line and applications with cycled production machines. Numerous predefined commands and operating modes for the most common application scenarios also reduce the programming effort in the PLC. Grouping data and various data export options usually eliminate the need for middleware. When using HF bus mode, mixed operation of HF and UHF read/write heads is still possible on the other RFID channels.
For the first time with encapsulated RFID readers up to ATEX zone 1/21
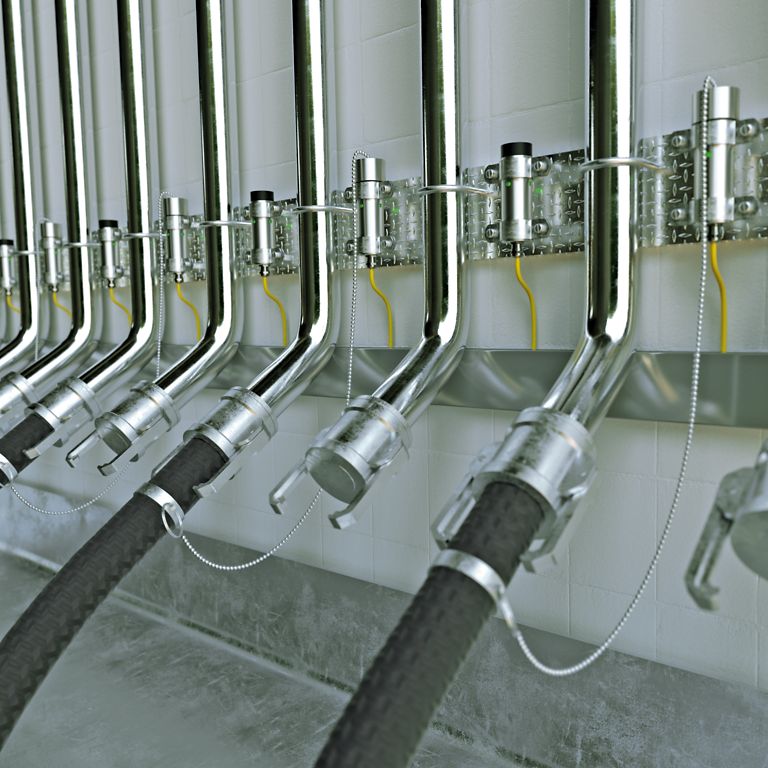
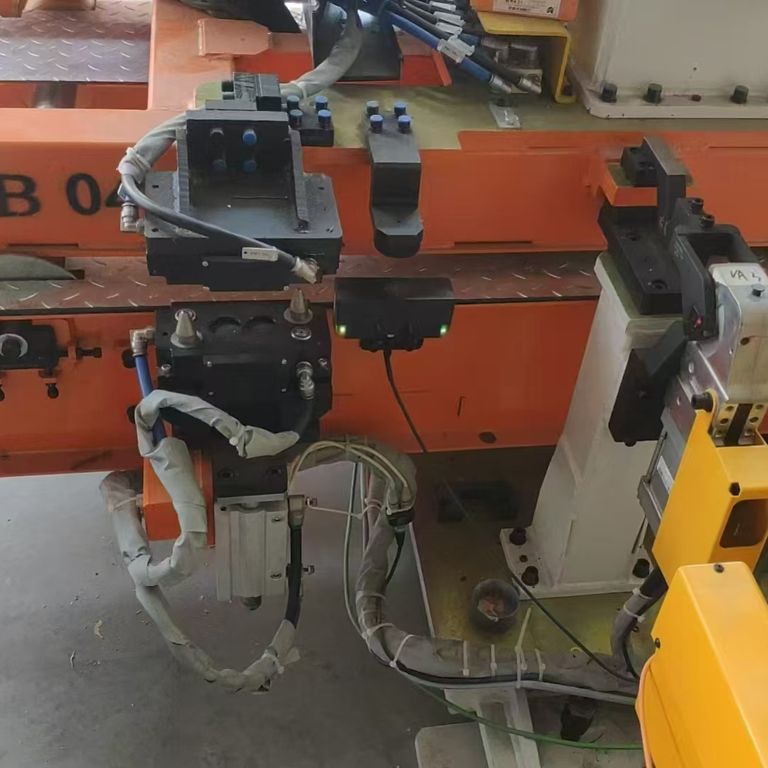
With the TN-R42/TC-Ex, TURCK has the world's only HF RFID read/write head that is certified for direct use in ATEX zone 1/21. In contrast to known pressure-encapsulated identification solutions for zone 1/21, the encapsulated reader can be easily integrated into confined applications due to its compact design. This makes the RFID reader ideal for contactless identification of correct hose and flange connections at coupling stations. Tags with a password function are also available for high data security and access protection requirements.
Now that the bus mode has also been approved for use in zone 1/21, TURCK can offer a complete portfolio of non-Ex and Ex devices in bus mode. As the TN-R42/TC-Ex behaves like a standard read/write head on the interface side, the user always has the same look and feel with regard to the connection and configuration of the entire system, regardless of whether it is used in explosive or non-explosive areas. In explosion-proof operation, only the last node in the bus line must be a device with a resistor as a termination. And the number of read/write heads that can be connected in bus mode is limited in Ex mode: For the ultra-compact TBEN-S interface, there are only five readers and for the TBEN-L interface, there are ten readers per channel.
Protective housings allow use in ATEX zone 2
To ensure reliable operation of the IP67 RFID interfaces and I/O modules of the TBEN-L, TBEN-S, TBEC product families or the IMC isolating switching amplifier in hazardous areas, TURCK has developed a stainless steel protective housing concept. The protective housing encloses the module approved for this use and its connections, thus protecting against mechanical damage or unintentional disconnection of the connections. This means that all specifications for the use of the devices in ATEX zone 2 are met.
Reduced commissioning effort
Thanks to the integrated TURCK RFID data interface with cyclic process data transmission, the user benefits from fast and easy access to HF and UHF functions, such as idle mode. The bus-capable HF RFID read/write heads can also be addressed automatically by simply activating the read/write head addresses in the parameters of the data interface. This allows users to save time compared to conventional methods, as they can connect the read/write heads one after the other and these are addressed automatically. In addition, bus addresses for bus-capable HF read/write heads can be set and queried via the TBEN-S-RFID via web server/PACTware. This allows the user to quickly check the correct commissioning of the bus mode without using an interface converter.
Hose coupling station, ink cartridges, format and tool change
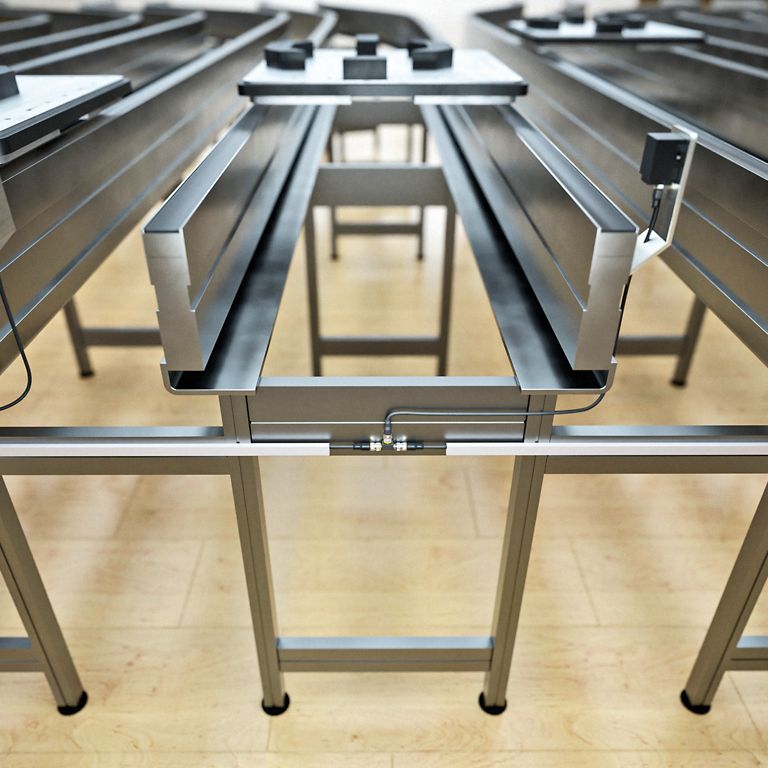
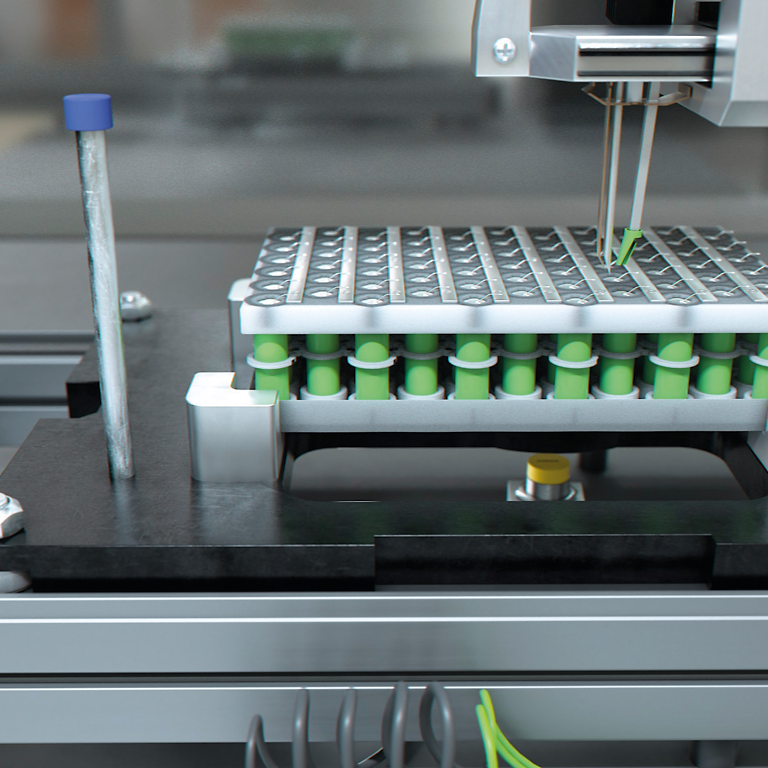
The HF bus mode is already being used successfully in practice – for example in female connector and hose coupling stations in the chemical, pharmaceutical and food industries. Swapped or leaking media can have serious consequences for plant safety, product quality or the health of employees and customers. If, for example, acid gets into an incorrect tank, there is a high risk potential. In order to ensure the correct connection between the hose and the corresponding connection point, TURCK offers a complete HF-RFID solution, in which the HF bus mode contributes significantly to the efficient implementation. Once the read/write heads have detected the intended hose connection, the opening signal is sent to the valve and pump. Thanks to RFID, information such as the date and time of the last hose cleaning can also be transmitted. Thanks to TURCK's TNR42/TC-Ex HF RFID read/write head, it is also possible to use the device in explosion-hazardous areas (zone 1/21). Rounding out the solution package are various tag types tailored to specific application requirements, including a glass variant for use in aggressive environments. RFID tags can also be inserted directly into a metal cap or connected to a clamp.
Another field of application is the identification of ink cartridges. The containers are automatically identified by the read/write heads in order to reliably prevent faulty print products and production downtimes. In addition, the system can remind the operator to change a color in time. The system calculates the time of the message based on the installation time and expiry date of an ink cartridge. In addition, the current ink consumption is used to approximately calculate the fill level of each individual container.
In many other applications, users benefit from HF bus mode and the option of connecting many HF readers quickly and cost-effectively. These include machines with several format and change tools, which can record and document the detection of the correct tool for a specific work step. Another aspect of this solution is the protection of plagiarism. This means that both machine builders and users benefit from the safety and increased service life that the use of original tools and original consumables such as oil or air filters brings.
However, new business models are also possible, such as charging for machine usage rather than selling the machine, by billing for tools, format parts, or consumables. For this purpose, the machine manufacturer could set up an automatic consignment warehouse at the user's premises. As soon as a component is inserted into the machine, it receives a message and ensures that materials are supplied further. However, this concept only works if only genuine parts are used.
Author | René Steiner is Business Development Manager RFID at TURCK